Description:
This example illustrates the calculation of the airflow in a model of the human airways reconstructed from CT images. The reconstruction was done using a region growing segmentation algorithm followed by iso-surface extraction.
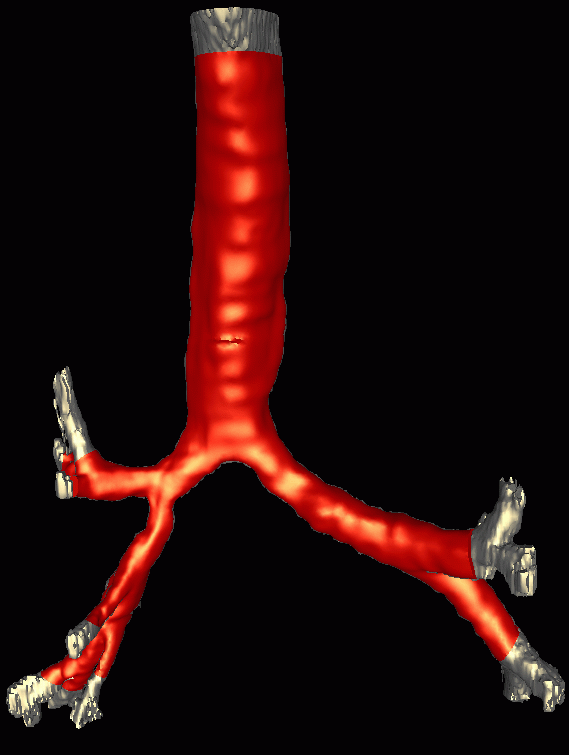
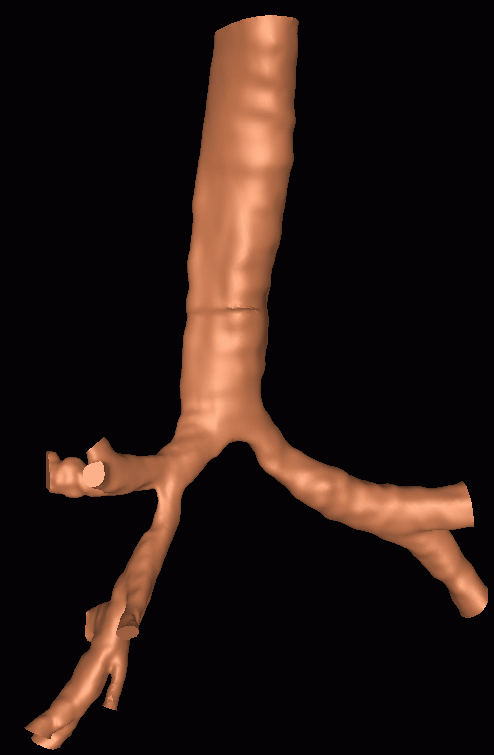
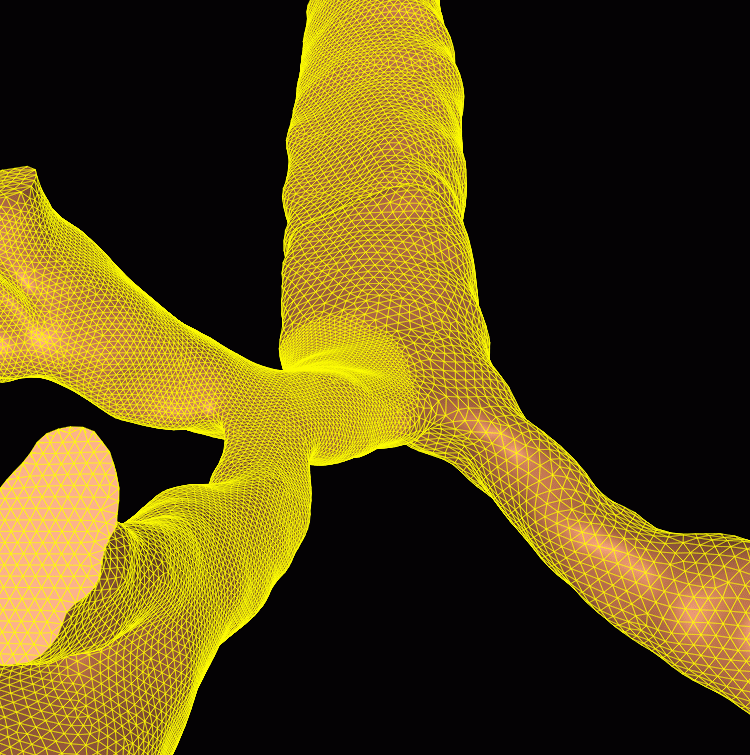
The following images show the reconstructed surface and cuts performed to limit the calculation to the proximal bronchi, the smoothed surface model used for unstructured grid generation and the generated finite element grid:



Steady Calculation
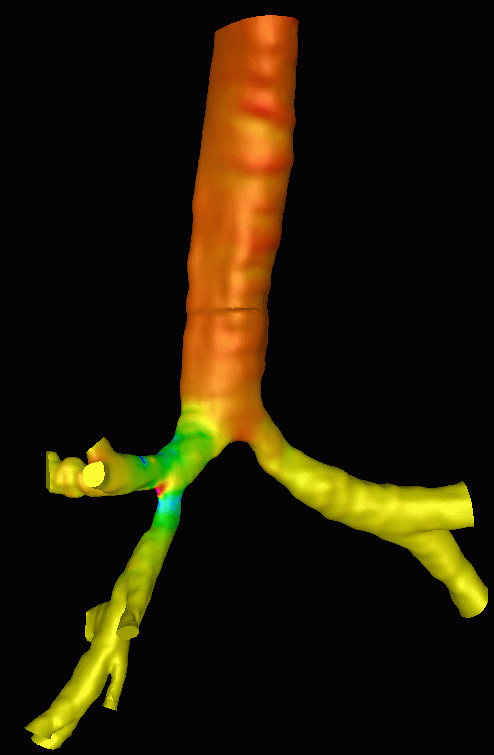
A calculation of the steady flow during inspiration was performed. The following images show the computed pressure drops. Note the increased pressure drop at the stenosis.
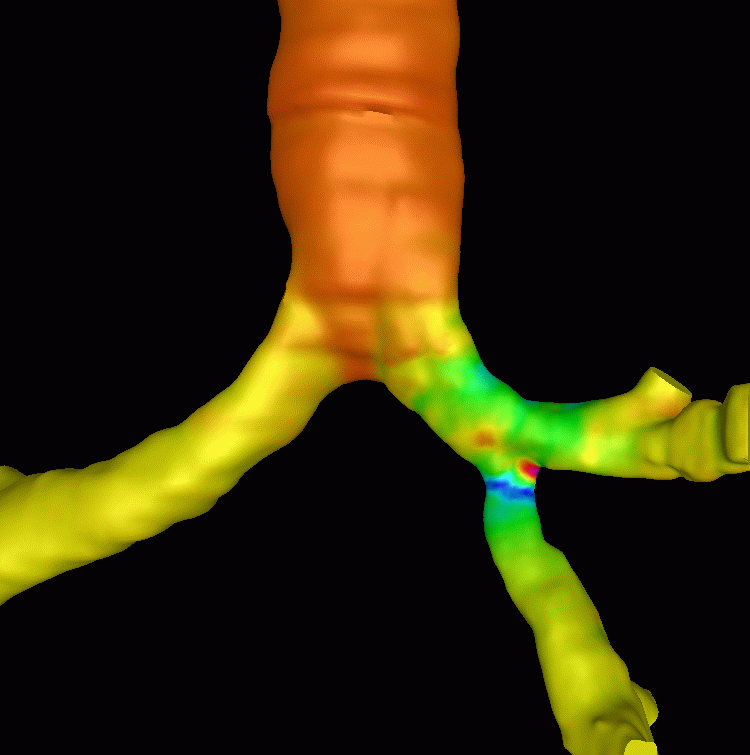
Flow visualizations in the region of the stenosis using streamlines colored according to velocity magnitude and flow division are shown below:


Unsteady Calculation
An unsteady respiratory calculation was then performed. The following images show pressure drops at different times during inspiration and expiration, note the reversal in the pressure drop from inspiration to expiration:
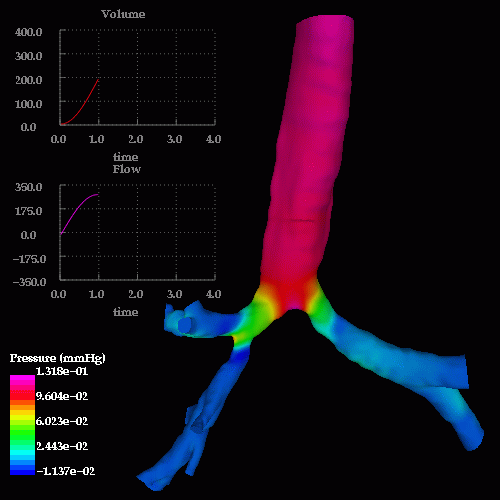
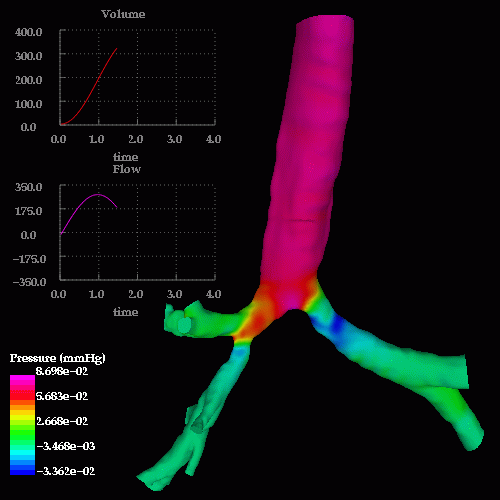
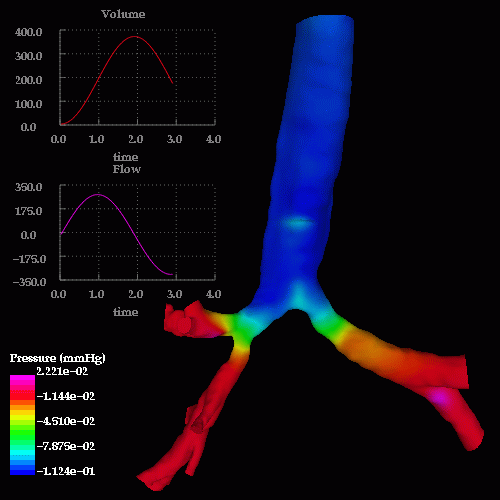
The following images show a detail of the pressure drop in the region of the stenosis:
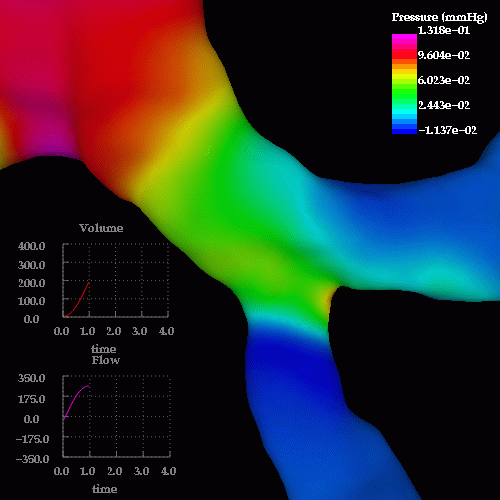
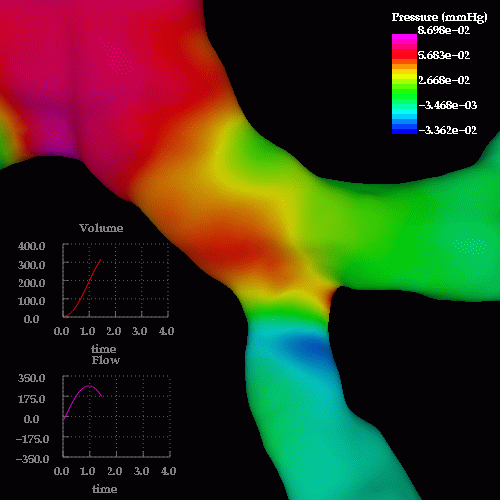
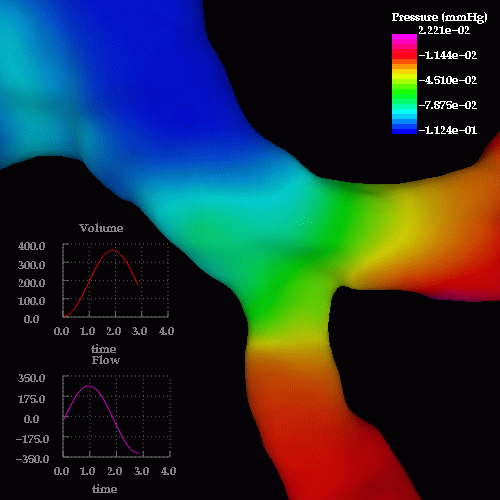
The following images show the wall shear stress at the same instants of time:
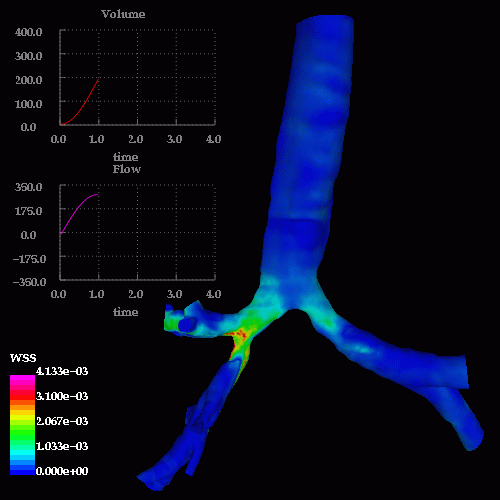
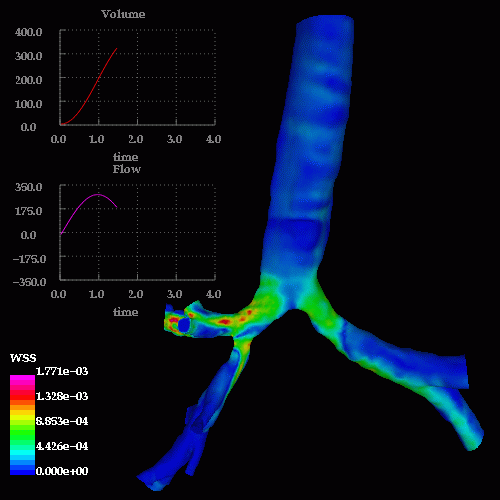
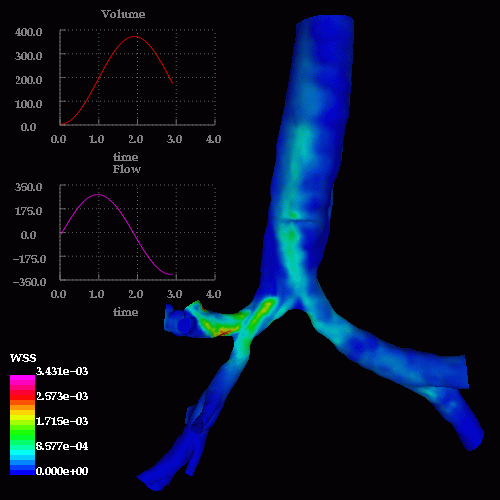
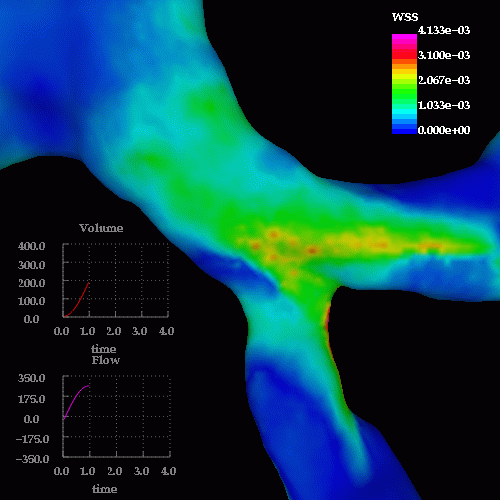
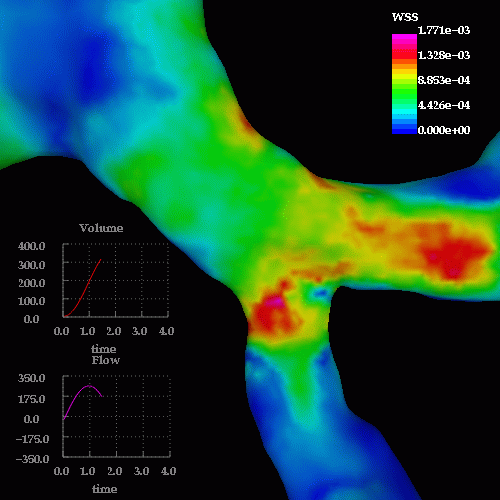
A detail of the wall shear stress in the region of the stenosis is shown below:
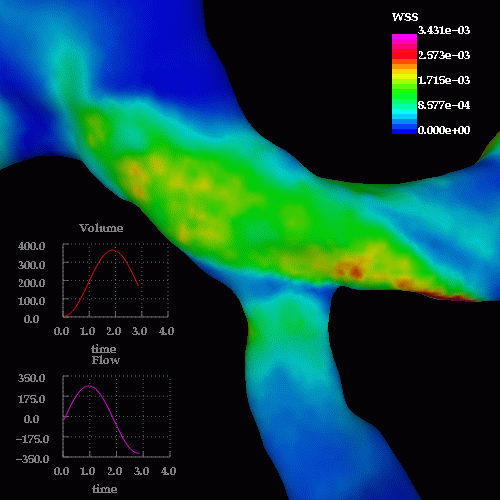
Velocity magnitudes in a cut through the stenosis are shown below at the same time instants:
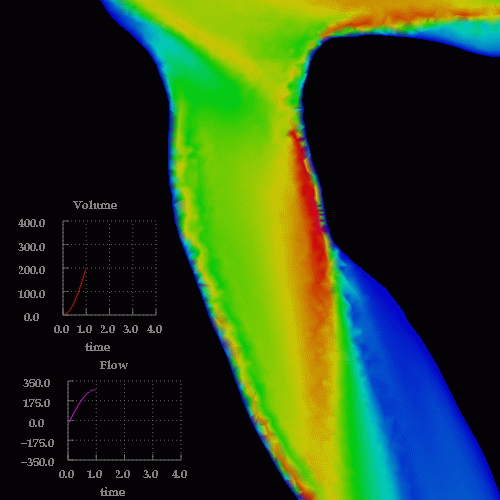
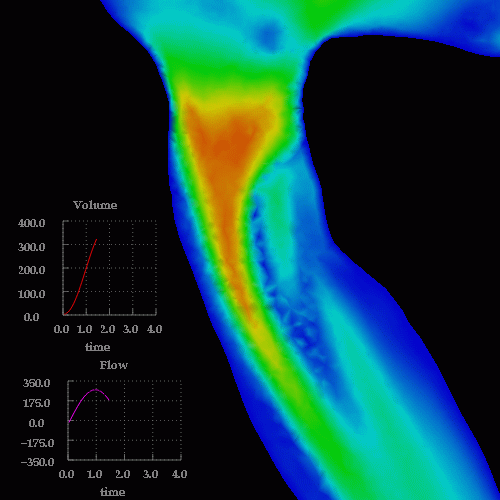
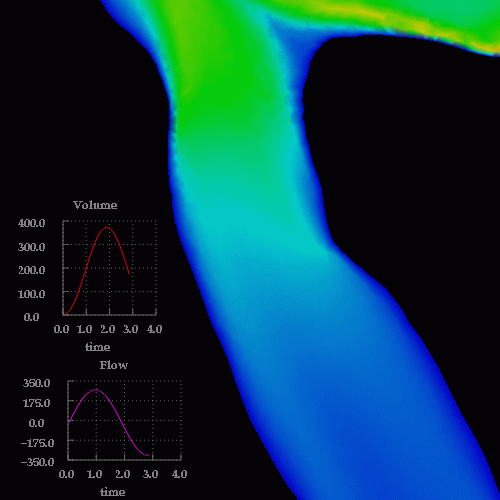
Velocity profiles in cuts through the stenosis are shown below:
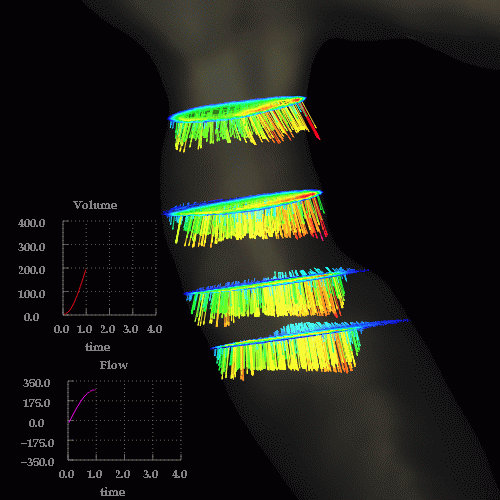
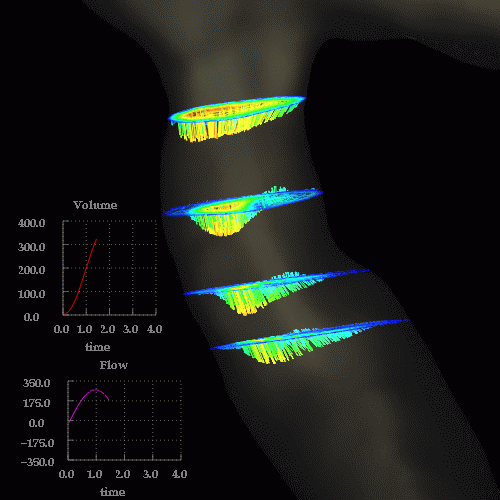
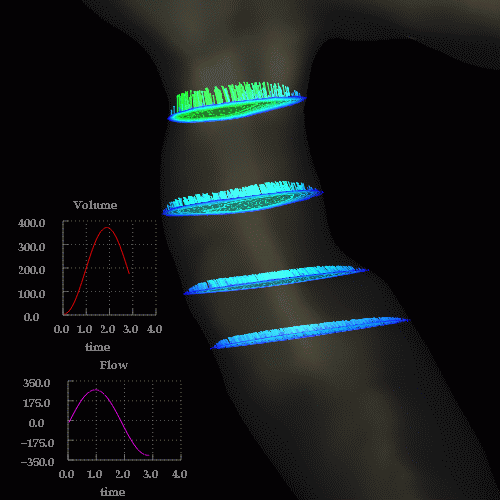
Observations: