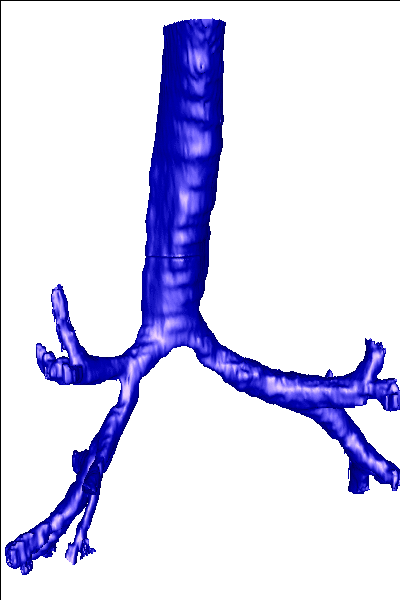



Description:
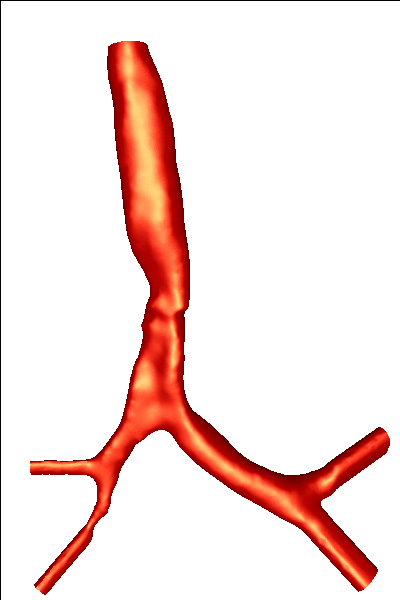
This example illustrates the calculation of the unsteady airflow in four models of the human airways with stenosis reconstructed from CT images. The reconstruction was done using a region growing segmentation algorithm followed by iso-surface extraction. The reconstructed models are shown below:




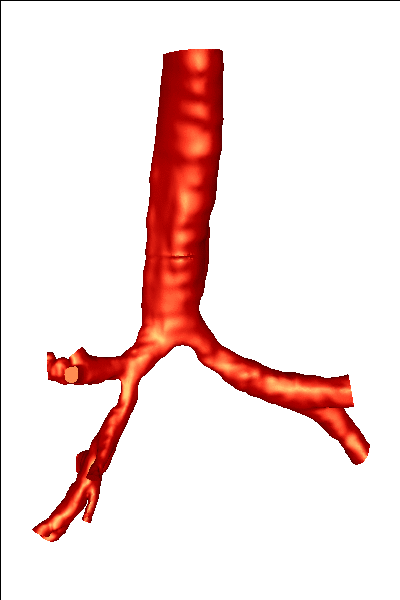
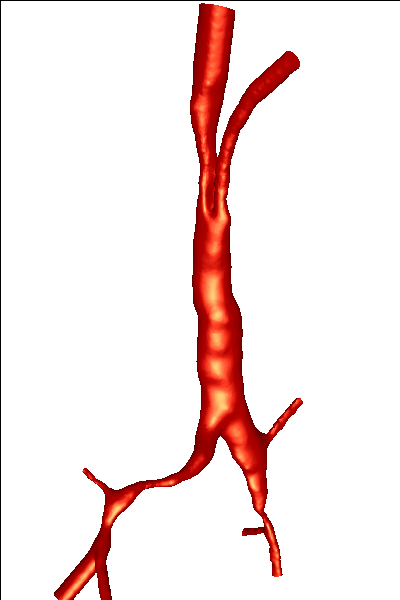
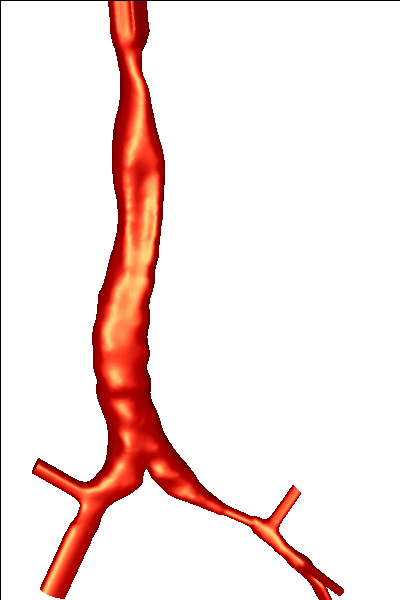
The reconstructed surfaces were then processed in order to generate finite element grids.The surfaces were first repaired using a volumetric technique, then smoothed, cut perpendicularly to the axis of the bronchi and extruded in order to minimize boundary condition effects. The final models are shown below:
Finite element grids were then generated from these surface
triangulations using an advancing front method. The resulting
tetrahedral grids have an element size distribution suitable for finite
element calculations. The images below show a detail of the grid
generation process:
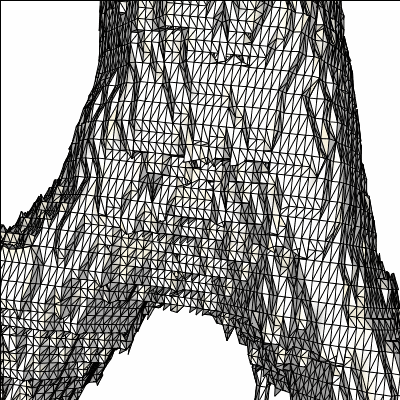
original reconstructed model
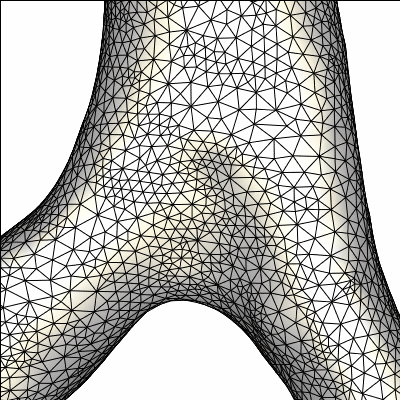
model after repair and smoothing
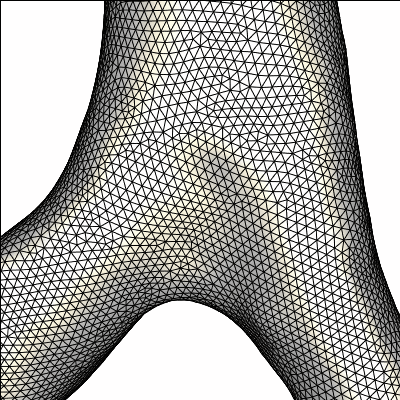
finite element grid
The following pictures show visualizations of the regions of high speed flow during inspiration and during expiration:
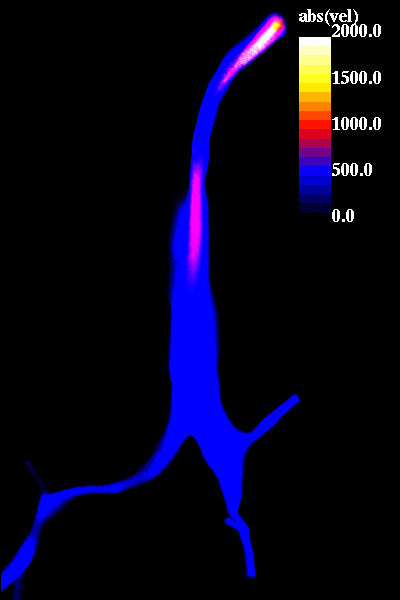
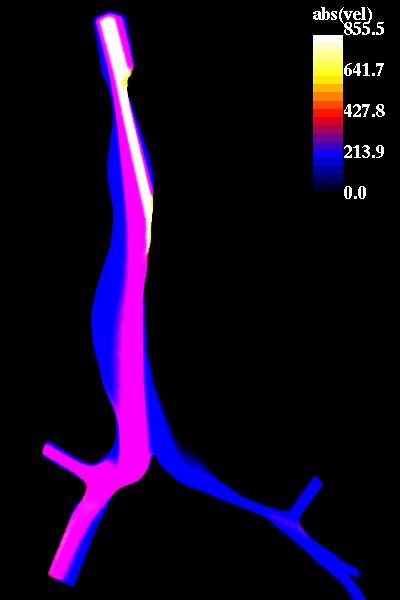
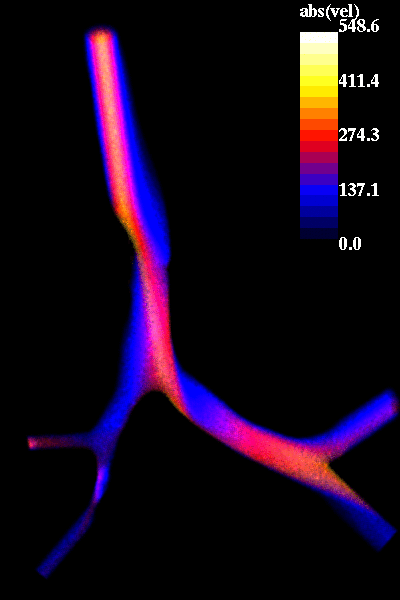
inspiration phase
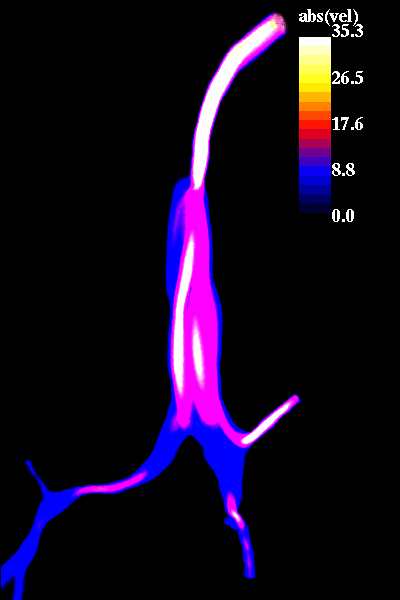
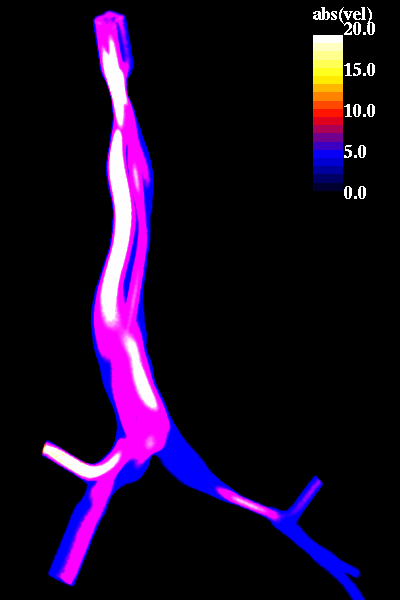
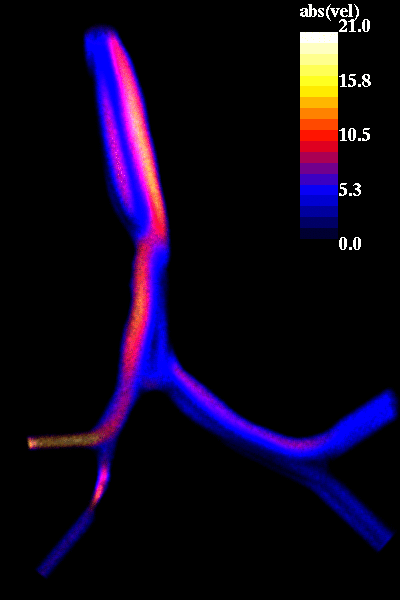
expiration phase
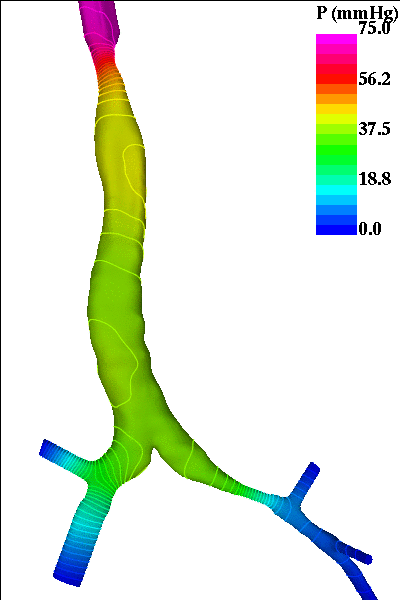
The following pictures show visualizations of the pressure drop during inspiration and during expiration (note the inversion of the pressure gradient during exhalation):
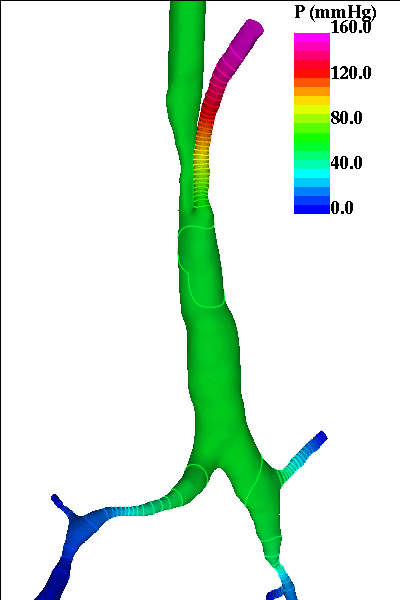
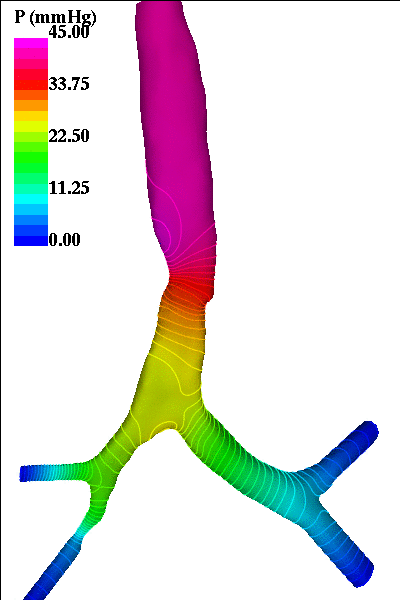
inspiration phase
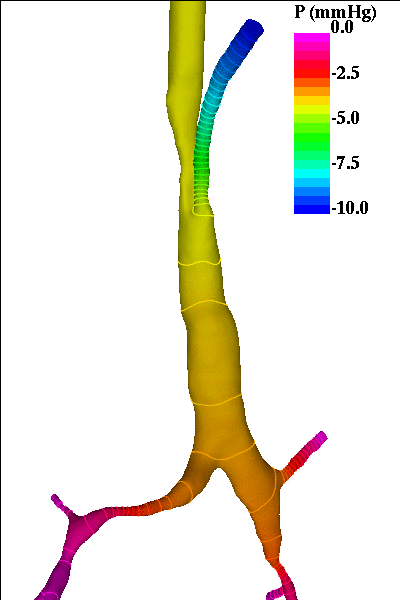
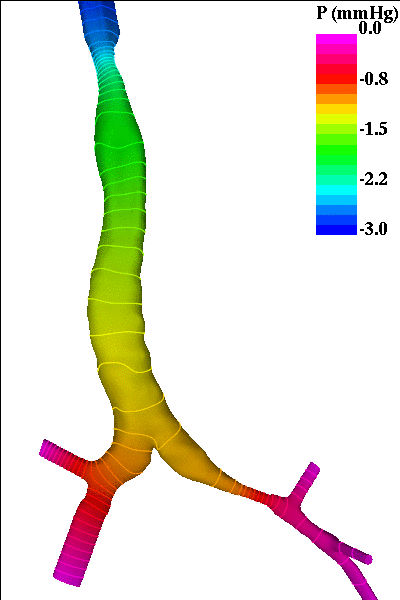
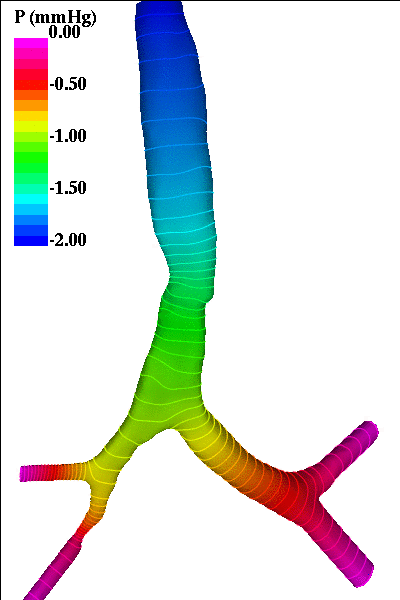
expiration phase