Description:
This example shows the generation of unstructured grids for finite element calculations of blood flow in carotid arteries reconstructed from contrast-enhanced MRA images. Each individual arterial branch is reconstructed using a deformable model which yields a surface triangulation for each branch. These branches are then merged using an adaptive voxelization technique. The finite element grid generation is then directly performed starting with the surface triangulation.
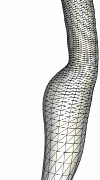
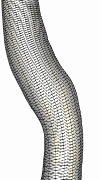
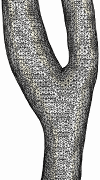
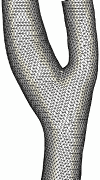
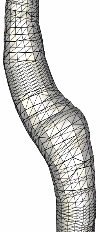
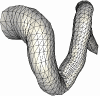
The following series of images show the merging of the surface triangulations corresponding to different branches of the carotid artery (internal, external and common) of a normal subject. The first image shows a portion of the external and common while the second figure shows a portion of the internal and common. The next two figures show the merged model and the surface of the generated finite element grid, respectively.




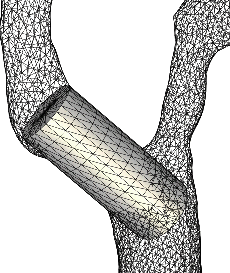
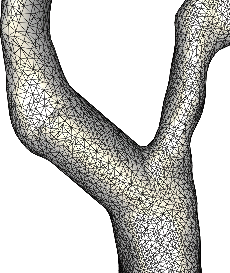
The second example shows the mergin of three branches of the carotid artery of a normal subject.

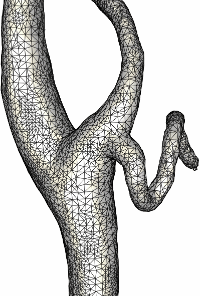
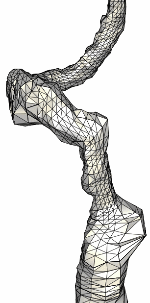
The next example shows the case of a patient with carotid artery stenosis
in the internal carotid artery.
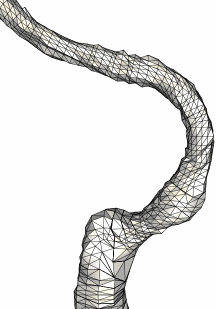
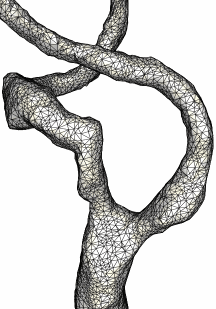
The following series of images show how the implantation of a stent in the stenosis can be simulated. The stenotic region of the internal carotid artery as well as the geometry of the stent are shown in the following two images.
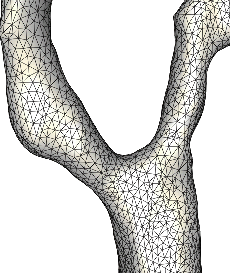
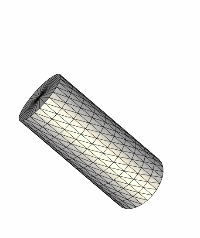
The next two images show the relative position of the stent and the final geometrical model after implanting the stent, respectively.
Observations: